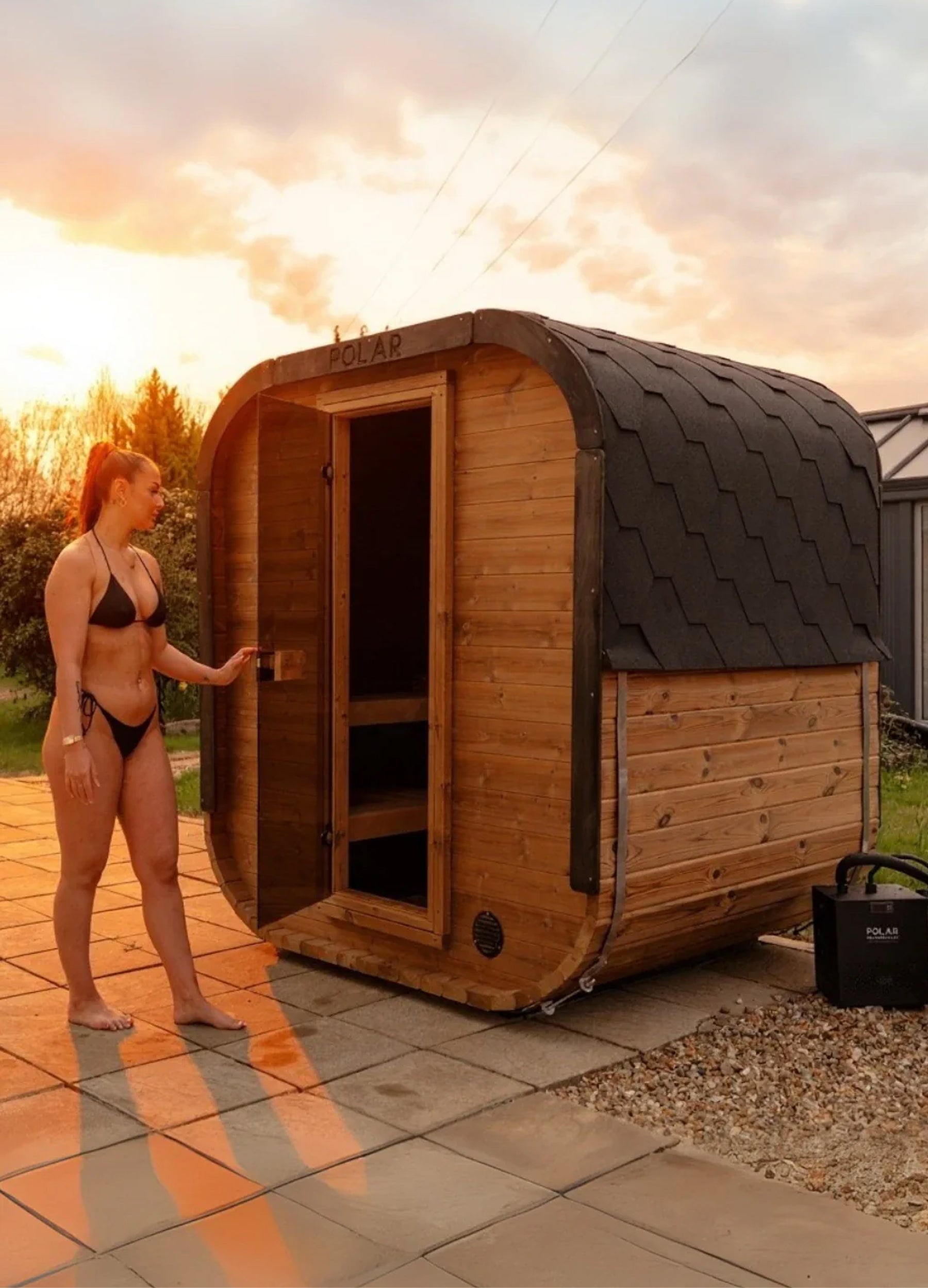
SAUNA HEALTH BENEFITS
Regular ice baths help reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression by stimulating the vagus nerve and increasing mood-boosting neurotransmitters like dopamine. One study found that young adults who immersed themselves in chest-deep cold baths experienced improved mood and higher energy levels compared to those who did not
A 2017 study showed that many medical professionals consider ice baths useful for basic post-sport recovery. Cold water immersion enhances blood circulation through vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation, efficiently delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing metabolic waste.
A review 2019 review of research papers from Texas A&M University found cold water therapy reduces inflammation by constricting blood vessels and limiting the flow of inflammatory compounds to affected areas. It also stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Regular cold water baths can effectively manage inflammation, promoting faster recovery and overall well-being.
Cold water's numbing effect temporarily blocks pain signals by slowing down nerve conduction velocity. Reduced inflammation and improved circulation also contribute to long-term pain relief. A recent study showed significant and prolonged increases in dopamine when people were in cool water for about an hour, which may contribute to pain relief
Regular cold water exposure reduces stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms by stimulating the vagus nerve and releasing mood-boosting neurotransmitters like dopamine. A study with young adults found that chest-deep cold water immersion improved mood scores and energy compared to those who did not immerse in cold water.
Cold water immersion triggers hormesis, a beneficial stress response that stimulates the immune system. It increases the production of white blood cells and stimulates the release of cytokines. A study with Finnish winter swimmers reported decreased tension and fatigue, improved mood, and memory compared to non-swimmers after regular cold water immersion.
Recent research shows that cold water exposure activates brown adipose tissue (BAT), which burns calories to generate heat through non-shivering thermogenesis. This increases metabolic rate and supports fat loss. Cold water therapy also improves insulin sensitivity, helping regulate blood sugar levels and prevent excess fat storage.
A scientific paper from 2016 shows cold water immersion stimulates the release of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters, increasing alertness, reducing fatigue, and improving mental clarity. It also enhances ATP production, sustaining energy levels throughout the day. Improved circulation delivers oxygen and nutrients to the brain and other organs more efficiently, further supporting cognitive function and overall energy levels